This article describes step by step how to set up jobs with GitLab‘s continuous integration (CI) tools for building and deploying a static website generated with Pelican. The source of the website needs to be hosted (publicly or privately) on GitLab.
As an example, this page is the result of the current master branch. For each change on a remote branch on GitLab, the website gets build as a test. If there is a change on the branch “master”, an additional job deploys the website to an external web server using the file transfer protocol (FTP). The full script as described below can be found in my website repository: .gitlab-ci.yml.
Requirements
- all used python modules should be mentioned by a requirements file placed in the root directory of the repository (It is called requirements.txt for this project).
- basic Git knowledge
- a GitLab account. CI tools for all open source projects are free, but there is also limited free access for private projects.
Set up continuous integration (CI)
We create a file called .gitlab-ci.yml in the root directory of the repository. It describes the jobs executed by the runner on changes in a branch in the remote repository (hosted on GitLab).
Preparing the build environment
The file .gitlab-ci.yml starts with defining a docker image. I chose the latest Ubuntu image ubuntu:latest just because of Ubuntu’s popularity.
image: ubuntu:latest
|
The minimal Ubuntu environment needs some packages in order to allow us to use Python. We specify what should be installed before executing any job:
before_script:
- apt update -qq && apt install -y -qq git python-pip
- git submodule update --init
- pip install virtualenv -q
- virtualenv pelican
- source pelican/bin/activate
- pip install -q -r requirements.txt
|
Before any job, the following happens:
- updating Ubuntu and installing
gitandpip(we needgitfor updating all submodules, e.g., themes and plugins, you can skip that if you don’t use submodules) - creating a virtual environment to allow for installing specific versions of Python packages independent of global system packages
- installing all Python packages required by your website
Creating a job for building the website
We define a job build website for building the pelican site. If the site gets build without errors, the job is successful. The line stage: build is optional.
build website:
stage: build
script:
- pelican content -o output -s pelicanconf.py
|
You can already merge all three sections into one YAML file called .gitlab-ci.yml, add it to your root of your project and push it to the remote repository on GitLab.
The output under CI/CD ➔ Pipelines will look like the following, with the job build website still running.
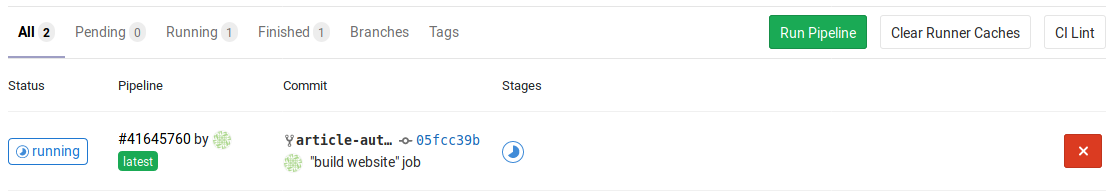
When the job is done successfully, i.e., the website was built, the sign changes to a green tick:
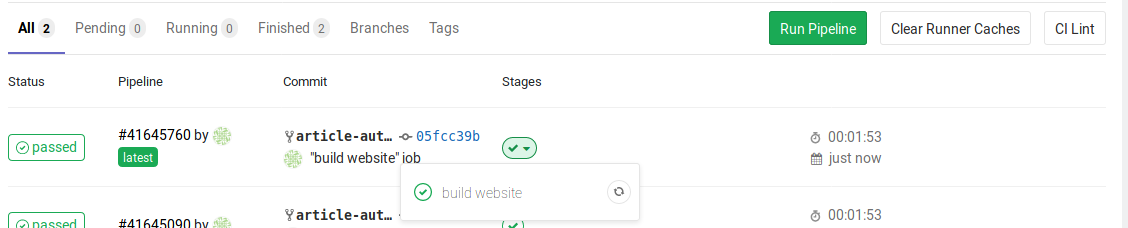
Refer to the full output for the job #139894076 of the pipeline #41645760 for details.
Deploying the built website with FTP
If we change the master branch, the same job build website gets triggered. In addition, I want to deploy the web site to an external web server if the job build website was successful.
The additional job is called deploy website.
deploy website:
stage: deploy
only:
- master
script:
- pelican content -o output -s publishconf.py
- apt install -y -qq lftp
- lftp $FTP_SERVER -u $FTP_USER,$FTP_PASS -e "mirror -R output/ / ; quit"
|
What’s happening in deploy website:
- the job gets assigned to the
deploystage - we define that this job gets triggered only in the branch “master”
- we build the page with the “publishconf.py” settings
- we install the client
lftp lftpgets triggered so that the code is uploaded to an external web server via ftp
The commit and the job execution is shown in commit 32e8161e. Although both jobs are part of the .gitlab-ci.yml, only one has been triggered as we pushed to the branch “article-auto-deploy” (i.e., not to the branch “master”).
However, when merged into master, the pipeline consists of two stages as can be seen here:
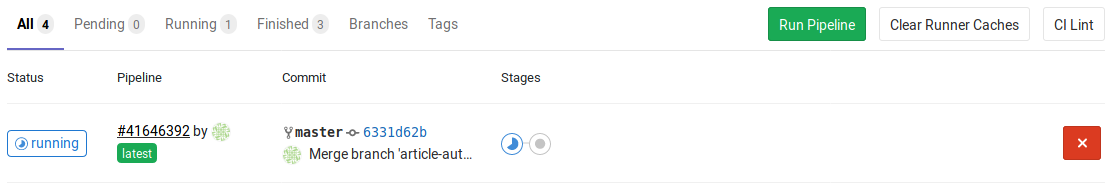
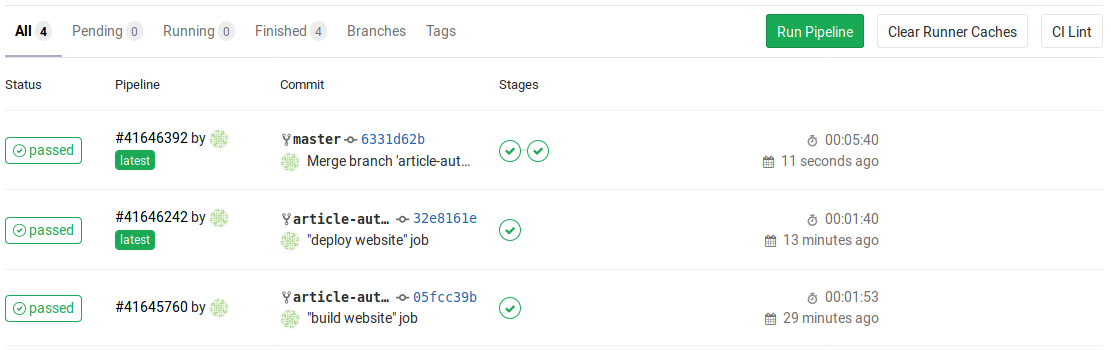
In the following, all three executions after each commit are shown. Only when the branch “article-auto-deploy” was merged into “master”, both jobs got triggered:
Setting up environment variables
You will notice environment variables (e.g. $FTP_PASS) in the upper example. As the file .gitlab-ci.yml can be publicly accessible in our repo, we don’t want everybody to see our credentials for the server. I firstly set up a dedicated FTP user on my server. I’ll then used the GitLab feature Settings ➔ CI/CD ➔ Variables for setting up variables as follows:
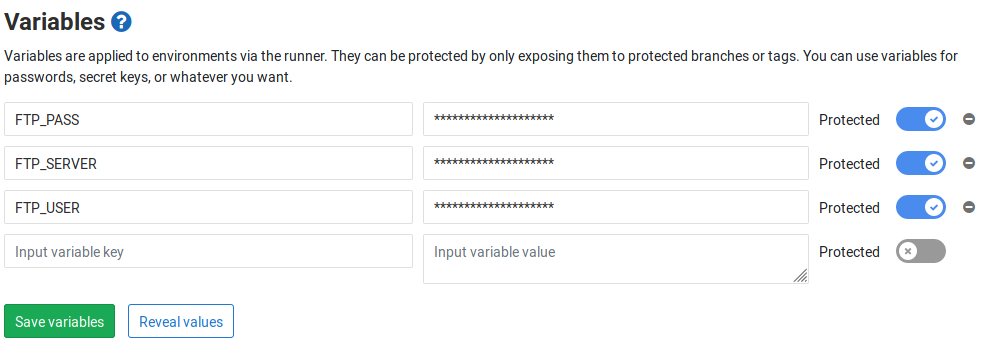
I made those variables only accessible to my protected branch master. Otherwise, everybody with access to another branch might be able to adapt the YAML file and retrieve my FTP password with putting echo $FTP_PASS one of the jobs.
Troubleshooting
Runner
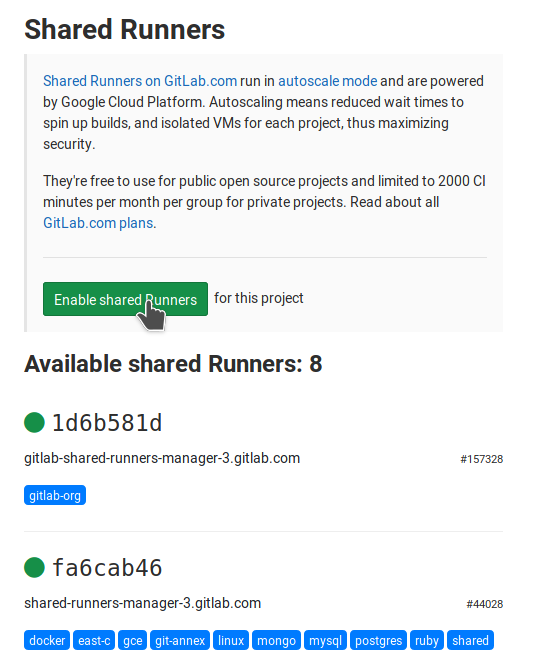
We use GitLab’s Shared Runners for a quick start. They are enabled by default on newer GitLab versions. Check if they are enabled under Settings ➔ CI/CD ➔ Runners. In the image below, you see that the runner #44028 comes with docker pre-installed:
More information
- Runners: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/ci/runners/README.html.
- GitLab’s CI quick start: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/ci/quick_start/
